p:: Database
mongo Shell Quick Reference
Basic Shell JavaScript Operations
| JavaScript Database Operations | Description |
|---|---|
db.auth() | If running in secure mode, authenticate the user. |
coll = db.<collection> | Set a specific collection in the current database to a variable coll |
db.collection.find() | Find all documents in the collection and returns a cursor. |
db.collection.insertOne() | Insert a new document into the collection. |
db.collection.insertMany() | Insert multiple new documents into the collection. |
db.collection.updateOne() | Update a single existing document in the collection. |
db.collection.updateMany() | Update multiple existing documents in the collection. |
db.collection.save() | Insert either a new document or update an existing document in the collection. |
db.collection.deleteOne() | Delete a single document from the collection. |
db.collection.deleteMany() | Delete documents from the collection. |
db.collection.drop() | Drops or removes completely the collection. |
db.collection.createIndex() | Create a new index on the collection if the index does not exist. |
db.getSiblingDB() | Return a reference to another database using this same connection without explicitly switching the current database. This allows for cross database queries. |
Queries
| Read Operations | Description |
|---|---|
db.collection.find(<query>) | Find the documents matching the <query> criteria in the collection. |
db.collection.find(<query>, <projection>) | Find documents matching the <query> criteria and return just specific fields in the <projection>. |
db.collection.find().sort(<sort order>) | Return results in the specified <sort order>. |
db.collection.find(<query>).sort(<sort order>) | Return the documents matching the <query> criteria in the specified <sort order>. |
db.collection.find( ... ).limit( <n> ) | Limit result to <n> rows. |
db.collection.find( ... ).skip( <n> ) | Skip <n> results. |
db.collection.count() | Returns total number of documents in the collection. |
db.collection.find(<query>).count() | Returns the total number of documents that match the query. |
db.collection.findOne(<query>) | Find and return a single document. Returns null if not found. |
SQL to MongoDB Mapping Chart
Terminology and Concepts
| SQL Terms/Concepts | MongoDB Terms/Concepts |
|---|---|
| database | database |
| table | collection |
| row | document or BSON document |
| column | field |
| index | index |
| table | joins $lookup, embedded documents |
| primary key | primary key |
| aggregation | (e.g. group by) aggregation pipeline |
| transactions | transactions |
Executables
| MongoDB | MySQL | Oracle | Informix | DB2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Database Server | mongod | mysqld | oracle | IDS | DB2 Server |
| Database Client | mongo | mysql | sqlplus | DB-Access | DB2 Client |
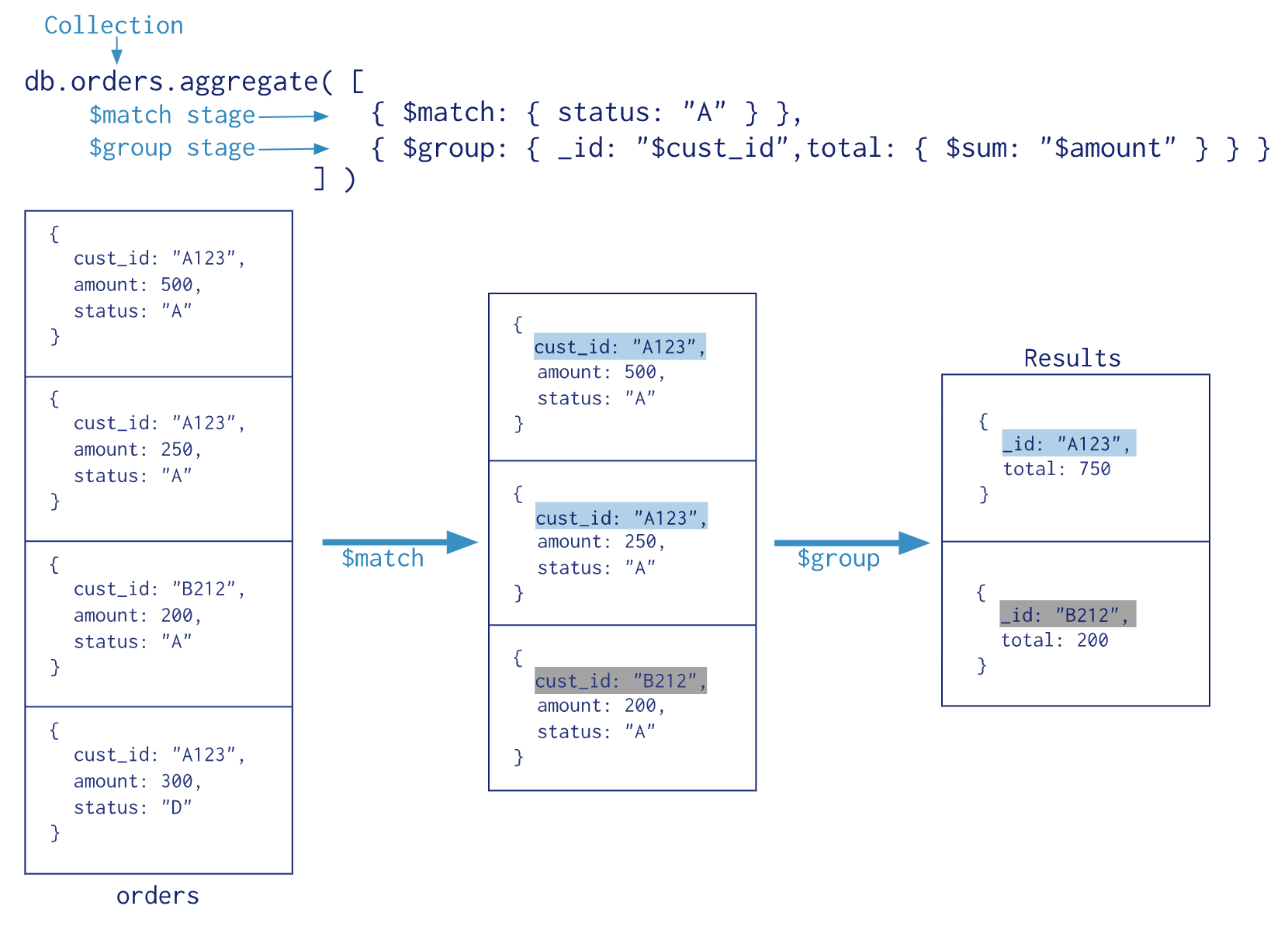
Aggregation
Aggregation operations process data records and return computed results. MongoDB provides three ways to perform aggregation: the aggregation pipeline, the map-reduce function, and single purpose aggregation methods.
Aggregation Pipeline
The aggregation pipeline is a framework for data aggregation modeled on the concept of data processing pipelines. Documents enter a multi-stage pipeline that transforms the documents into aggregated results. Each stage transforms the documents as they pass through the pipeline.
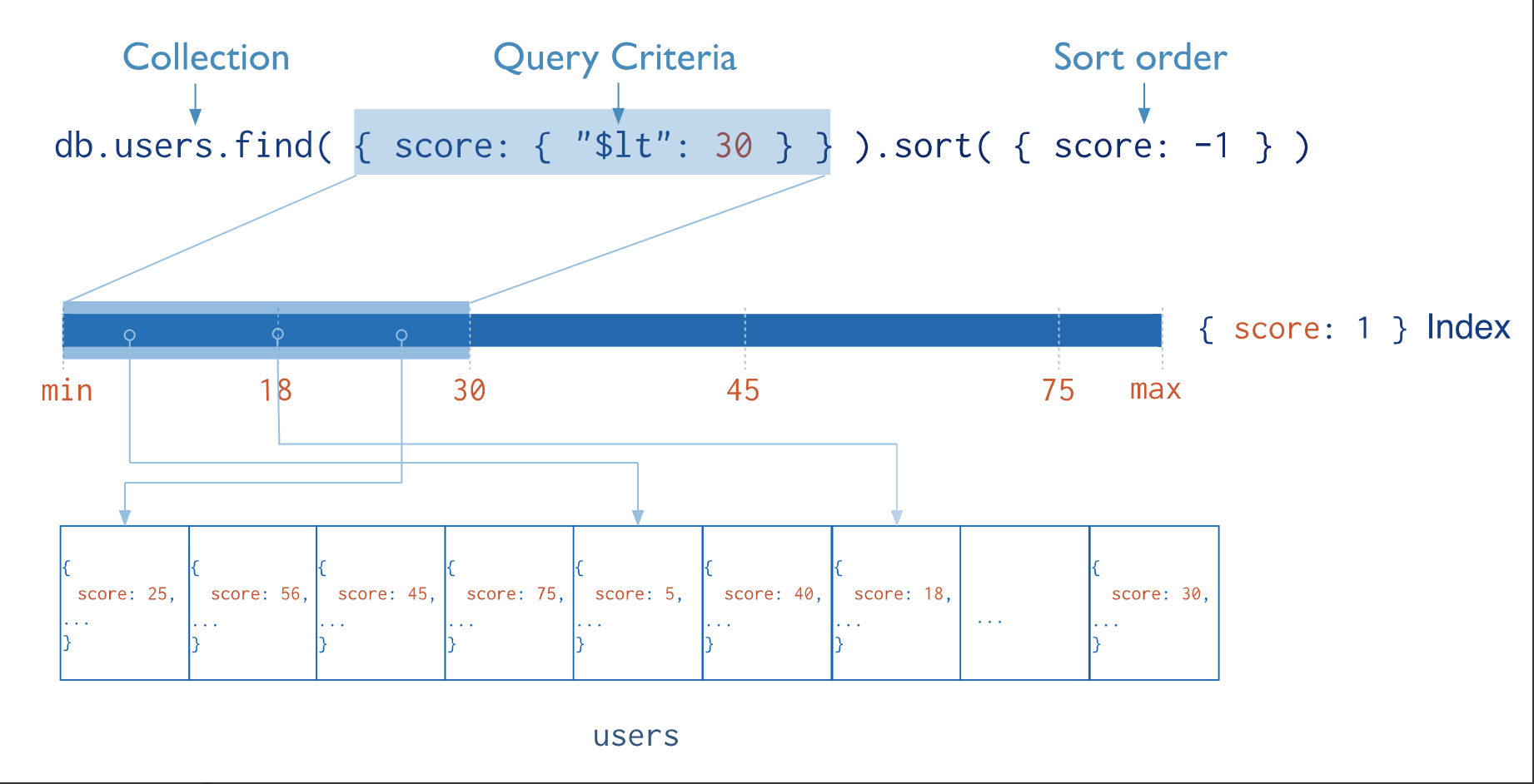
Indexes
Indexes support the efficient execution of queries in MongoDB. Without indexes, MongoDB must perform a collection scan, i.e. scan every document in a collection, to select those documents that match the query statement. If an appropriate index exists for a query, MongoDB can use the index to limit the number of documents it must inspect.
Index Types
- Single Field
- Compound Index
- Multikey Index
- Geospatial Index
- Text Indexes
Index Properties
- Unique Indexes
- Partial Indexes
- Sparse Indexes
- TTL Indexes
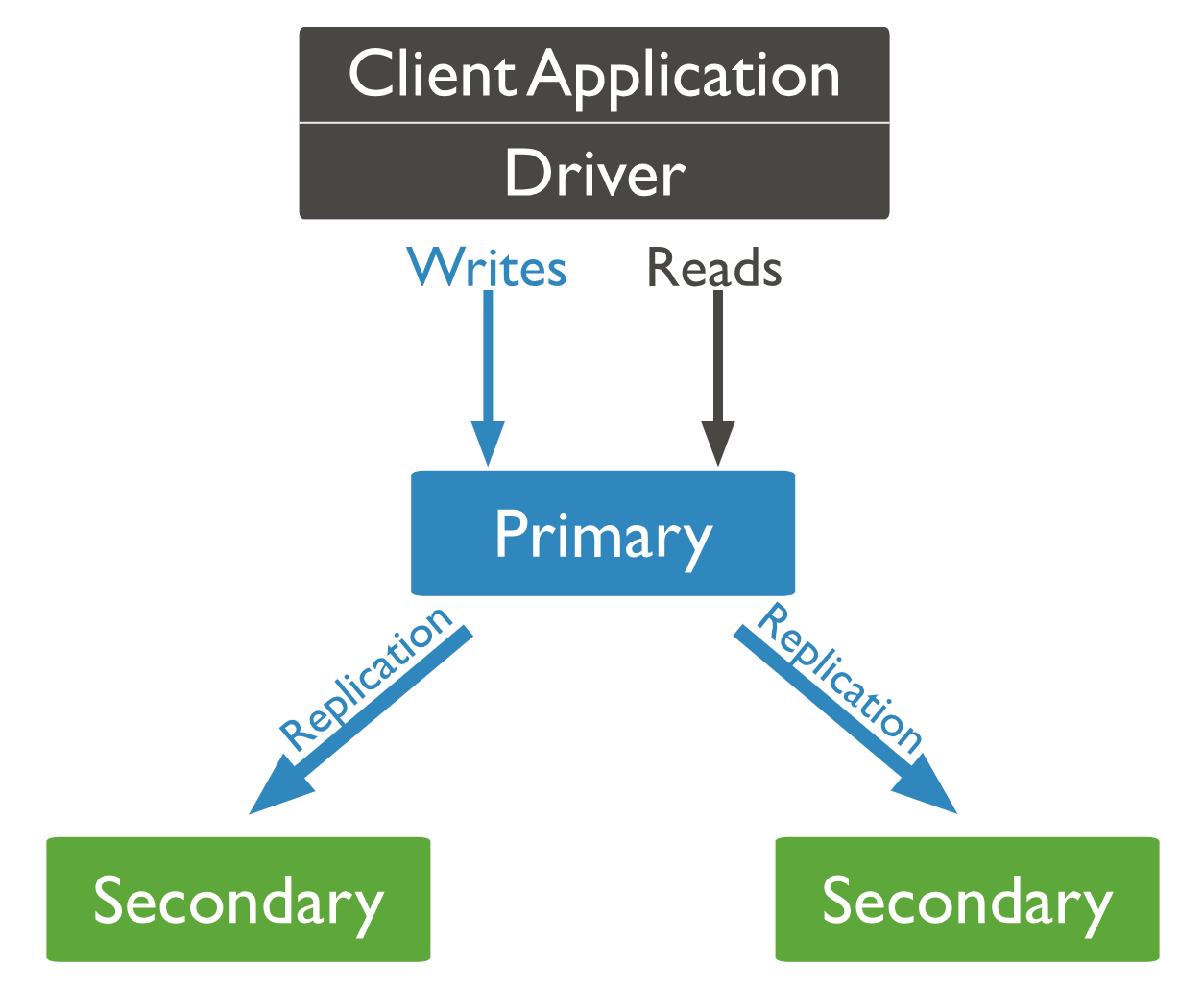
Replication
A replica set in MongoDB is a group of mongod processes that maintain the same data set. Replica sets provide redundancy and high availability, and are the basis for all production deployments.
The members of a replica set are:
- Primary: The primary receives all write operations.
- Secondaries: Secondaries replicate operations from the primary to maintain an identical data set.
Replication in MongoDB
A replica set is a group of mongod instances that maintain the same data set. A replica set contains several data bearing nodes and optionally one arbiter node. Of the data bearing nodes, one and only one member is deemed the primary node, while the other nodes are deemed secondary nodes.
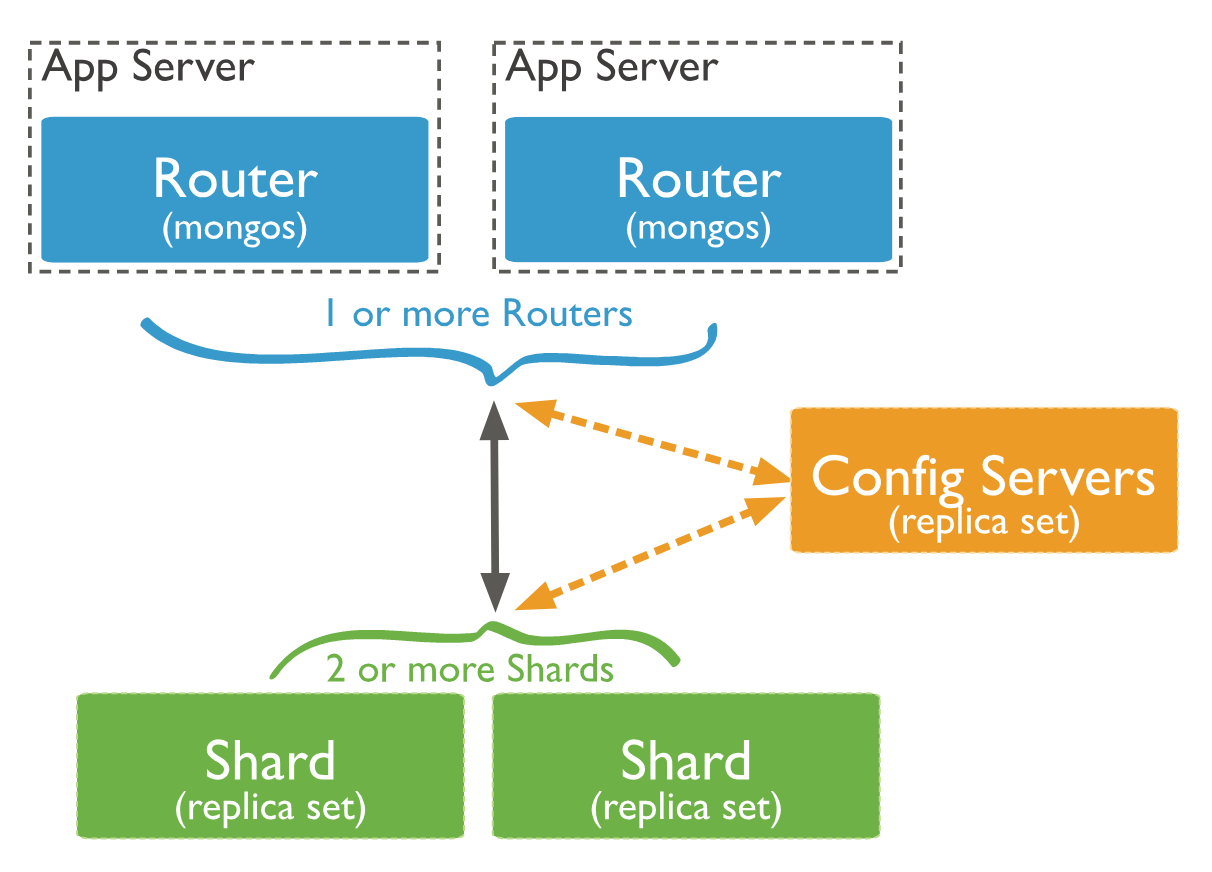
Sharding
Sharding is a method for distributing data across multiple machines. MongoDB uses sharding to support deployments with very large data sets and high throughput operations.
Sharded Cluster
A MongoDB sharded cluster consists of the following components:
- shard: Each shard contains a subset of the sharded data. Each shard can be deployed as a replica set.
- mongos: The mongos acts as a query router, providing an interface between client applications and the sharded cluster.
- config servers: Config servers store metadata and configuration settings for the cluster.
Shard Keys
The shard key determines the distribution of the collection’s documents among the cluster’s shards. The shard key is either an indexed field or indexed compound fields that exists in every document in the collection.
Zones
In sharded clusters, you can create zones of sharded data based on the shard key. In a balanced cluster, MongoDB migrates chunks covered by a zone only to those shards associated with the zone.